Linux Active Directory with DNS ,DHCP, Group Policies and Print Services
Requirements and Specifications
DNS Service
- DNS should provide a mechanism to store and resolve domain names. It should also store the information about the various servers deployed at Server Room. Solution should provide a primary and secondary DNS server. It should also cache the DNS records for better bandwidth utilization.
- It should support DNS zone storage in Directory Server
- It should support conditional DNS forwarders e.g. forwarding based on a DNS Domain name in the query.
- It should support Round robin on all resource record (RR)
DHCP Service
- DHCP server should provide the mechanism for allocating IP address to various clients and computers in network. Vendor should provide a DHCP server with a valid IP addressing scheme. However servers will have a static IP addressing scheme.
- It should support DHCP database/file for backup and restore
- It should provide support for multi-cast scopes
- It should support Integration of DHCP with DNS
Print Server service
- It should support Role based access
- It should support Quota deployment
- It should support and integrate with Directory server and printer allocation/configuration should be done through policy services
- It should support reports/ monitoring, Auditing and tracking
- It should support centralized allocation /DE-allocation of Network printers to the users.
- It should support prioritizing, queuing and spooling
- It should support multiple end user operating systems – e.g. Linux all flavors (Desktop OS and Server OS, Windows 7 and higher, Windows server 2003 and higher, Mac OS
Directory Service
- Directory Services based on LDAP Version 3/Kerberos.-Should be complied
- Modify (Add, Delete, Replace)- The product should accept modify requests and perform the operations, including additions, deletions, and replacements.
- Manage & Create Users using LDAP- The product should comply with LDAP Version 3.0 and support the LDAP directory and can create the user and store the user-level information. It should also have the capability of managing the user.
- Search - The product should accept search requests and perform the requested search operations.
- Definition of Object Classes - The product should associate entries with object classes in accordance with the X.500 model.
- Distinguished Name - The product should correctly encode and decode protocol representations of distinguished names.
- Definition of Matching Rules - The product should support matching rules in accordance with the X.500 model.
- Parsing - The product should correctly parse string representations of distinguished names.
- SSL over TCP as the Transporting Protocol - Product should implement mapping of LDAP over SSL over TCP and provides a protocol listener IP port 636
- Password Aging - The password aging System will force the user to change the password in every "x" days. The number of days will be directly managed at the administrator level and also as per the user group.
- Application Integration with Directory Services - The product should have the provision to get integrated with third party application with Directory Services for Authentication & Authorization.
- Solution needs to support dual stack of Ipv4 and Ipv6 .
Integrated Components
The following components will be used for building up the Integrated Environment .
- BIND (Berkeley Internet Name Domain) is an implementation of the DNS protocols and provides an openly redistributable reference implementation of the major components of the Domain Name System, including:
- Domain Name System server
- Domain Name System resolver library
- Tools for managing and verifying the proper operation of the DNS server
Some of the important features of BIND9 are DNS Security (DNSSEC, TSIG), IPv6, DNS Protocol Enhancements (IXFR, DDNS, DNS Notify, EDNS0), Views, Multiprocessor Support,Replications,Zone updates and an Improved Portability Architecture.
- ISC (Internet Systems Consortium) DHCP is open source software that implements the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol for connection to an IP network. It is production-grade software that offers a complete solution for implementing DHCP servers, relay agents, and clients for small local networks to large enterprises. ISC DHCP solution supports both IPv4 and IPv6, and is suitable for use in high-volume and high-reliability applications.
- Directory and policy - Samba 4.X is a milestone release that brings Active Directory functionality to the open source SMB/CIFS (Server Message Block/Common Internet File System) file and print server. Samba 4.X can serve as an Active Directory Domain Controller, provide DNS services, handle Kerberos-based authentication, and administer group policy. The Samba 4.X Domain Controller can even be managed using the native Windows Active Directory admin tools. Supports DC and ADC .
- Common UNIX Printing System (CUPS). This printing system is a freely available, portable printing layer which has become the new standard for printing in most Linux distribution. CUPS manages print jobs and queues and provides network printing using the standard Internet Printing Protocol (IPP), while offering support for a very large range of printers, from dot-matrix to laser and many in between. CUPS also supports Post Script Printer Description (PPD) and auto-detection of network printers, and features a simple web-based configuration and administration tool.
DNS Structure
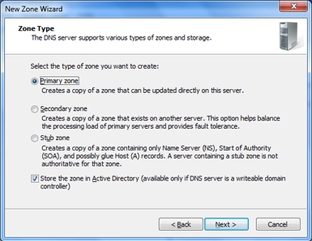
As there will be Linux AD implemented via SAMBA4 , DNS which is Bind9 is Additionally installed and integrated with SAMBA4 implementation . The DNS setup and records will be managed by DNS MMC Snap-In tool on windows as shown below .
Adding new records, Updating existing records , Deleting , Changing zone properties , Defining Zone Replication Scope, Reverse Lookup Zone, Dynamic Update etc will be created and deployed via Window's DNS MMC Snap-in tool from Windows Management Machine placed in management zone .
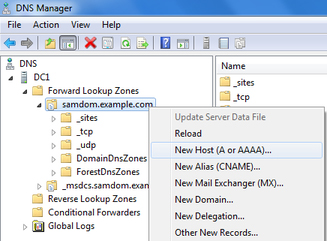
The DNS can also be managed via Linux CLI .
An Separate DNS zone for Servers is created for having name based resolution for inter communications .
Bind9 with Master – Slave replication is designed . The Slave will reside on ADC and replicated .
Both IPV4 and IPV6 as dual stack will be activated and populated .
Conditional Forwarding
A forwarder is a Domain Name System (DNS) server on a network that is used to forward DNS queries for external DNS names to DNS servers outside that network. You can also configure your server to forward queries according to specific domain names using conditional forwarders .
Bind9 supports forwarders and conditional forwarding . Conditional forwarders are not implemented yet on Samba integrated DNS management Snap-In . That means any conditional forwarders will be implemented via CLI .
Round robin DNS
Round Robin DNS is a technique of load distribution, load balancing, or fault-tolerance provisioning multiple, redundant Internet Protocol service hosts, e.g., Web server, FTP servers, by managing the Domain Name System's (DNS) responses to address requests from client computers according to an appropriate statistical model.
Bind9 support Round robin ( RR ) for long . Both IPV4 and IPv6 is supported over round robin principle. The records are output as per rrset-order . rrset-order defines the order in which multiple records of the same type are returned. This works for any record type in which the records are similar not just A or AAAA RRs and covers results in the ANSWER SECTION and the ADDITIONAL SECTION. The default is cyclic (round-robin).
DHCP Structure
DHCP will be configured on IPV4 and IPV6 both as dual stack . Dedicated 2 VMs is allocated for High availability . Following are the details of suggested DHCP environment
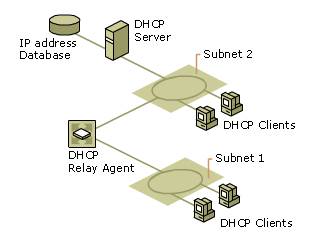
- Enablement of both dhcpd and dhcpv6d Services for ipv4 and ipv6 respectively
- Only Desktop / Laptop User based VLAN and IP Telephone Devices VLAN to be included in scoping of DHCP . Scope ID 242 to be configured for scope of IP Telephony devices .
- Switches will be activated as DHCP relay agent to forward the different VLAN Traffic for DHCP server .
- Both Ipv4 and Ipv6 scopes will be defined . Ipv6 will be preferred over ipv4 . As there will be around 200 devices which might increase up to 400 hundred , the lease period suggested for 8 hours.
- High Availability is inbuilt feature of ISC DHCP . It will configured as primary and secondary server in active / passive mode or fail-over mode
- The Leases databases is file type and can be backup and restored
- DHCP with dynamic DNS updates to ensure the tight integration of DNS with DHCP
Active Directory via SAMBA4
Samba AD DC Features
Samba4 will act as PDC and DC under active directory concept . This implementation will be emulating the windows 2008 R2 schema and equivalance. As AD environment is specific to Windows it will only manage windows infrastructure .
- LDAP
- Kerberos
- X.500 complaint
- Windows Domain Controller
- Centralized Identity Management Server
- Authentication
- Authorization
- SMB / SMB2 / CIFS
- Windows machines join AD natively
- Ipv4 and Ipv6 ready
- SSL over TCP as the Transporting Protocol ( https://wiki.samba.org/index.php/Configuring_LDAP_over_SSL_%28LDAPS%29_on_a_Samba_AD_DC )
- 7 FSMO roles
- PDC Emulator
- RID Master
- Schema Master
- Domain Naming Master
- Infrastructure Master
- Domain DNS Zone Master role
- Forest DNS Zone Master role
Forest and Domain design
Environment will have one domain controller in a domain and additional domain controllers to the domain is added to improve the availability and reliability of network services. Adding additional domain controllers can help provide fault tolerance, balance the load of existing domain controllers, and provide additional infrastructure support to sites.More than one domain controller in a domain makes it possible for the domain to continue to function if a domain controller fails or must be disconnected. Multiple domain controllers can also improve performance by making it easier for clients to connect to a domain controller when logging on to the network.
Distribution of FSMO roles for Active Directory DC and Addition DC will be
Active Directory DC
- PDC Emulator
- RID Master
- Schema Master
- Domain Naming Master
- Infrastructure Master
- Domain DNS Zone Master role
- Forest DNS Zone Master role
Addition DC
- PDC Emulator
- RID Master
- Infrastructure Master
In case of DC failure the ADC needs to be promoted as DC .
Time Synchronization
Time synchronization design and setup are very important for an Active Directory environment. This is because time synchronization issues lead to Kerberos authentication failures once the maximum tolerance for computer clock synchronization (By default is five (5) minutes) is exceeded.
We have 2 NTP servers running on RHEL for the time synchronization purpose . Active directory will update time or synchronize time from these NTP servers
AD Group Policies
Group Policy
The guiding principle for Group Policy design is OU design and IT administrative model and together they form the below benefits
- To enable delegation of administration
- To scope the application of Group Policy Objects
While designing the group policy the required consideration from key stake holders and best practices are consulted.
Group Policy settings are passed from parent containers down to child containers. This means that a policy that is applied to a parent container applies to all the containers including users and computers that are below the parent containers in the Active directory tree hierarchy.
However if you specifically assign a group policy for a child container that contradicts the parent container policy, the child container’s policy overrides the parent group policy. If policies are not contradictory, both are implemented. Group Policies are processed in the following order:
- Local Group policy
- Site Group Policy
- Domain Group Policy
- Organizational unit Group Policy
We are selecting No Override option so that child containers cannot override any policy setting set by higher level GPO. This option is not turned on by default and must be turned on in each GPO where it’s wanted. In Addition with Default Domain and Domain Controller policy will apply set of CIS (Center for Internet Security) recommended policy for Active Directory like Account, Audit, Security, Interactive Login, Event Log Settings, Network Services, Network Access, User Account Control etc
SAMBA integrated CUPS ( Print Server )
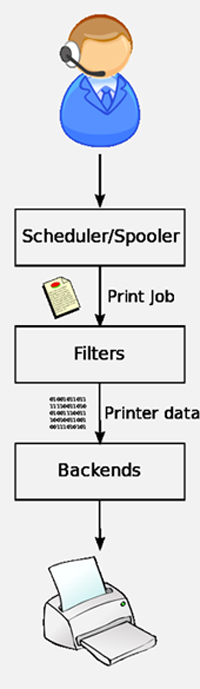
A print server accepts print jobs from network computers, queues them locally and then sends them to the appropriate printers. As well as having domain and file service capabilities, Samba can also act as a MS Windows compatible print server. While Samba provides the interface to Windows/SMB machines, CUPS or LDP is used by Samba to send print jobs to the devices.
CUPS provides a mechanism that allows print jobs to be sent to printers in a standard fashion. The print-data goes to a scheduler which sends jobs to a filter system that converts the print job into a format the printer will understand. The filter system then passes the data on to a backend—a special filter that sends print data to a device or network connection. The system makes extensive use of PostScript and rasterization of data to convert the data into a format suitable for the destination printer.
The CUPS scheduler implements Internet Printing Protocol (IPP) over HTTP/1.1. A helper application (cups-lpd) converts Line Printer Daemon protocol (LPD) requests to IPP. The scheduler also provides a web-based interface for managing print jobs, the configuration of the server, and for documentation about CUPS itself.
CUPS can process a variety of data formats on the print server. It converts the print-job data into the final language/format of the printer via a series of filters. It uses MIME types for identifying file formats.
The backends are the ways in which CUPS sends data to printers. There are several backends available for CUPS: parallel, serial, and USB ports, cups-pdf PDF Virtual Printing, as well as network backends that operate via the IPP, JetDirect (AppSocket), Line Printer Daemon ("LPD"), and SMB protocols.
CUPS integrated with SAMBA supports multiple end user operating systems – e.g. Linux all flavors (Desktop OS and Server OS, Windows 7 and higher, Windows server 2003 and higher, Mac OS.
CUPS web-based administration interface
On all platforms, CUPS has a web-based administration interface that runs on port 631. It particularly helps the need to monitor print jobs and add print queues and printers remotely. This interface is with an enhanced administration interface that allows users to add, modify, delete, configure, and control classes, jobs, and printers. It Supports reports/ monitoring, Auditing and tracking of print queues . It will also do the centralized allocation /DE-allocation of Network printers to the users.
CUPS supports page and size-based quotas for each printer. The quotas are tracked individually for each user, but a single set of limits applies to all users for a particular printer. CUPS logs every page that is printed on a system to the page_log file. Page logging is only available for drivers that provide page accounting information, typically all PostScript and CUPS raster devices. Raw queues and queues using third-party solutions such as Foomatic generally do not have useful page accounting information available.
Tetra is committed to working with enterprises, to bring its customers some of the very best data protection solutions. Our customers enjoy vast array of benefits, including special pricing, ongoing technical support and besides the quality of our software.
Tetra provides Open Source backup solution through Amada enterprise level several Open Source backup solution.
Allow our representative to either call you in 24 hours or E-Mail you for mobile details about our services - Click Here.
